L11 期权定价:B-S-M模型
- L11 期权定价:B-S-M模型
Wiener Processes and Itô's Lemma
Model the Dynamics of Stock Prices / Returns
ABC of Stochastic Processes
-
Stochastic Processes
- Describes the way in which a variable such as a stock price, exchange rate or interest rate changes through time
- Incorporates uncertainties
-
Example of Stochastic Processes
- Each day a stock price: increases by $1 with probability 30, stays the same with probability 50%, reduces by $1 with probability 20%
- Each day a stock price change is drawn from a normal distribution with mean $0.2 and standard deviation $1
-
Markov Processes
- In a Markov process future movements in a variable depend only on where we are, not the history of how we got to where we are
- Is the process followed by the temperature at a certain place Markov?
- We assume that stock prices follow Markov processes
-
Weak-Form Market Efficiency
- This asserts that it is impossible to produce consistently superior returns with a trading rule based on the past history of stock prices. In other words technical analysis does not work.
- A Markov process for stock prices is consistent with weak-form market efficiency
Variances & Standard Deviations
-
In Markov processes changes in successive periods of time are independent
-
This means that variances are additive
-
Standard deviations are not additive
-
In our example it is correct to say that the variance is 100 per year.
-
It is strictly speaking not correct to say that the standard deviation is 10 per year.
A Wiener Process
-
Define as a normal distribution with mean and variance
-
A variable follows a Wiener process if
- The change in in a small interval of time is
- where
- The values of for any different (non-overlapping) periods of time are independent
-
Properties of a Wiener Process
- Mean of is
- Variance of is
- Standard deviation of is
Norbert Wiener (诺伯特维纳)

Brownian Motion

Louis Bachelier (路易斯巴舍利耶)

Generalized Wiener Processes
-
A Wiener process has a drift rate (i.e. average change per unit time) of and a variance rate of
-
In a generalized Wiener process the drift rate and the variance rate can be set equal to any chosen constants
- Mean change in per unit time is
- Variance of change in per unit time is
-
Taking Limits
- What does an expression involving and mean?
- It should be interpreted as meaning that the corresponding expression involving and is true in the limit as tends to zero
- In this respect, stochastic calculus is analogous to ordinary calculus
Generalized Wiener Process
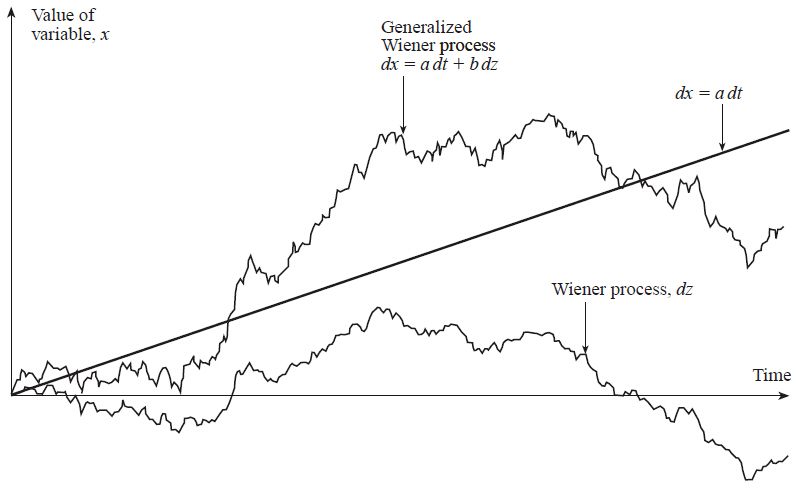
A Model for Stock Prices
-
It Process
- In an It process the drift rate and the variance rate are functions of time
- The discrete time equivalent is true in the limit as tends to zero
- In an It process the drift rate and the variance rate are functions of time
-
A generalized Wiener process is not appropriate for stocks
- For a stock price we can conjecture that its expected percentage change in a short period of time remains constant (not its expected actual change)
- We can also conjecture that our uncertainty as to the size of future stock price movements is proportional to the level of the stock price
-
Geometric Brownian Motion
It's lemma
Kiyosi It (伊藤清)
It's lemma
-
If we know the stochastic process followed by , It's lemma tells us the stochastic process followed by some function . When then
-
Since a derivative is a function of the price of the underlying asset and time, It's lemma plays an important part in the analysis of derivatives
-
Applications of It's Lemma to A Stock Price Process
- Suppose the stock price process is
- For a function of and we have
The Black-Scholes-Merton Model
The Stock Price Assumption
The Stock Price Assumption
-
Consider a stock whose price is
-
In a short period of time of length , the return on the stock is normally distributed:
-
So the price is lognormal distributed
or
Continuously Compounded Return
-
If is the realized continuously compounded return we have
-
The Expected Return
- The expected value of the stock price is
- The expected return on the stock is not
- The reason is that, and are not the same
-
vs.
- is the expected return in a very short time, , expressed with a compounding frequency of
- is the expected return in a long period of time expressed with continuous compounding (or, to a good approximation, with a compounding frequency of )
Volatility
-
The Volatility
- The volatility is the standard deviation of the continuously compounded rate of return in year
- The standard deviation of the return in a short time period time is approximately
- If a stock price is $50 and its volatility is 25% per year what is the standard deviation of the price change in one day?
-
Estimating Volatility
- Take observations at intervals of years (e.g. for weekly data )
- Calculate the continuously compounded return in each interval as:
- Calculate the standard deviation, , of the 's
- The historical volatility estimate is:
-
Nature of Volatility
- Volatility is usually much greater when the market is open (i.e. the asset is trading) than when it is closed
- For this reason time is usually measured in ``trading days'' not calendar days when options are valued
- It is assumed that there are trading days in one year for most assets
The Black-Scholes-Merton Model

Black-Scholes-Merton: The Big Idea
-
The option price and the stock price depend on the same underlying source of uncertainty
-
We can form a portfolio consisting of the stock and the option which eliminates this source of uncertainty
-
The portfolio is instantaneously riskless and must instantaneously earn the risk-free rate
-
This leads to the Black-Scholes-Merton differential equation
The Derivation of the Black-Scholes-Merton Differential Equation
-
Stock price & derivative price
-
Set up a portfolio
- derivative:
- shares:
-
The value of the portfolio
Since the portfolio is risk-free, we have
So, the Black-Scholes-Merton Differential Equation is
- Any security whose price is dependent on the stock price satisfies the differential equation
- The particular security being valued is determined by the boundary conditions of the differential equation
- In a forward contract the boundary condition is when
- The solution to the equation is
Black-Scholes-Merton Pricing for Options
where
- Properties of Black-Scholes Formula
- As becomes very large tends to and p tends to zero
- As becomes very small tends to zero and tends to
- What happens as becomes very large?
- What happens as becomes very large?
Understanding Black-Scholes
The formula
- : Discount rate
- : Probability of exercise
- : Expected percentage increase in stock price if option is exercised
- : Strike price paid if option is exercised
Risk-Neutral Valuation
Risk-Neutral Valuation
-
Risk-Neutral Valuation
- The variable does not appear in the Black-Scholes-Merton differential equation
- The equation is independent of all variables affected by risk preference
- The solution to the differential equation is therefore the same in a risk-free world as it is in the real world
- This leads to the principle of risk-neutral valuation
-
Applying Risk-Neutral Valuation
- [1] Assume that the expected return from the stock price is the risk-free rate
- [2] Calculate the expected payoff from the option
- [3] Discount at the risk-free rate
Option Sensitivities: Greeks
Greeks
The Taylor Expansion
- Delta:
- Gamma:
- Vega:
- Rho:
- Theta:
课后阅读与练习
课后阅读与练习
-
课后阅读:教材第十一章第三节、十二章第一节、第六章、第七章相关内容
-
练习
- 教材pp186:7,10
- 扫码做题
