区块链技术及其金融应用
区块链应用
区块链应用
区块链经济的的七大设计原则
| 原则 | 待解决的问题 | 突破性进展 | 影响 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 网络化诚信 | “双花” | 区块链共识机制 | 去中心化身份、去担保化、信任网络 |
| 分布式力量 | (中心化机构)滥用数据、篡改数据 | 去中心化 | 消除商业和社会治理中的信任危机 |
| 把价值作为激励 | 传统互联网价值分配不公 | 区块奖励 | 通证经济 |
| 安全性 | 数字隐私、黑客攻击 | 非对称加密技术 | 区块链安全、透明 |
| 隐私 | 个人数据容易被其他机构“监控”、收集 | 非许可、匿名 | 阻止了“监控社会” |
| 权利保护 | 传统互联网“中介机构”可能侵害参与者权益、维权成本高 | 区块链确权、智能合约——代码即法律 | 目标决定、执行过程、奖励机制透明化 |
| 普惠性 | 使用传统商业服务的成本 | 降低成本和许可要求 | 终结霸权、实现普惠 |
区块链的金融应用
八个核心功能
| FUNCTION | BLOCKCHAIN IMPACT | STAKEHOLDER |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Authenticating Identity and Value | Verifiable and robust identities, cryptographically secured | Rating agencies, consumer data analytics, marketing, retail banking, wholesale banking, payment card networks, regulators |
| 2. Moving Value—make a payment, transfer money, and purchase goods and services | Transfer of value in very large and very small increments without intermediary will dramatically reduce cost and speed of payments | Retail banking, wholesale banking, payment card networks, money transfer services, telecommunications, regulators |
| 3. Storing Value—currencies, commodities, and financial assets are stores of value. Safety deposit box, a savings account, or a checking account. Money market funds or Treasury bills | Payment mechanismcombined with a reliable and safe store of value reduces need for typical financial services; bank savings and checking accounts will become obsolete | Retail banking, brokerages, investment banking, asset management, telecommunications, regulators |
| 4. Lending Value—credit card debt, mortgages, corporate bonds, municipal bonds, government bonds, asset-backed securities, and other forms of credit | Debt can be issued, traded, and settled on the blockchain; increases efficiency, reduces friction, improves systemic risk. Consumers can use reputation to access loans from peers; significant for the world’s unbanked and for entrepreneurs | Wholesale, commercial, and retail banking, public finance (i.e., government finance), microlending, crowdfunding, regulators, credit rating agencies, credit score software companies |
| 5. Exchanging Value—speculating, hedging, and arbitraging. Matching orders, clearing trades, collateral management and valuation, settlement and custody | Blockchain takes settlement times on all transactions from days and weeks to minutes and seconds. This speed and efficiency also creates opportunities for unbanked and underbanked to participate in wealth creation | Investment, wholesale banking, foreign exchange traders, hedge funds, pension funds, retail brokerage, clearinghouses, stock, futures, commodities exchanges; commodities brokerages, central banks, regulators |
| 6. Funding and Investing in an Asset,Company, Start-up—capital appreciation, dividends, interest, rents, or some combination | New models for peer-to-peer financing, recording of corporate actions such as dividends paid automatically through smart contracts. Titles registry to automate claims to rental income and other forms of yield | Investment banking, venture capital, legal, audit, property management, stock exchanges, crowdfunding, regulators |
| 7. Insuring Value and Managing Risk—protect assets, homes, lives, health, business property, and business practices, derivative products | Using reputationalsystems, insurers will better estimate actuarial risk, creating decentralized markets for insurance. More transparent derivatives | Insurance, risk management, wholesale banking, brokerage, clearinghouses, regulators |
| 8. Accounting for Value—new corporate governance | Distributed ledger will make audit and financial reporting real time, responsive, and transparent, will dramatically improve capacity of regulators to scrutinize financial actions within a corporation | Audit, asset management, shareholder watchdogs, regulators |
区块链相关研究
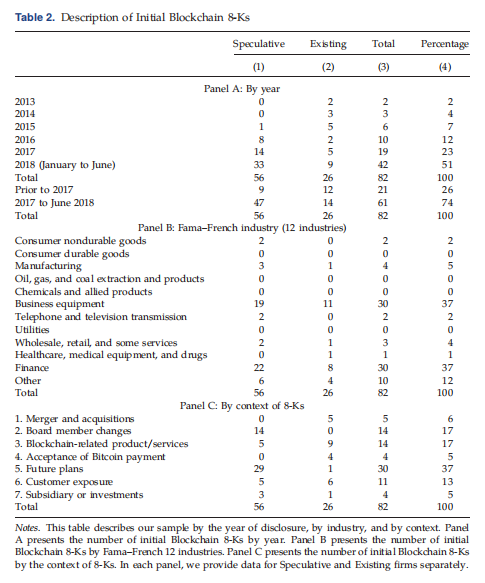
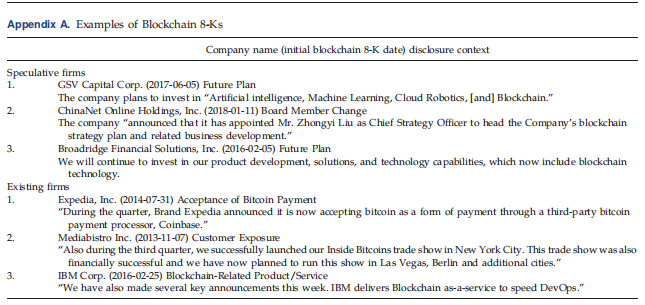
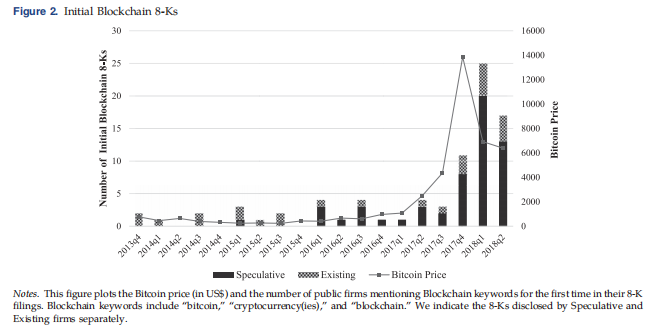
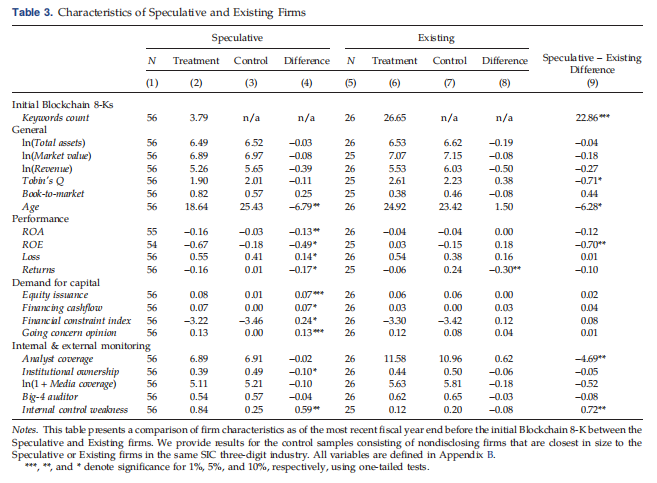
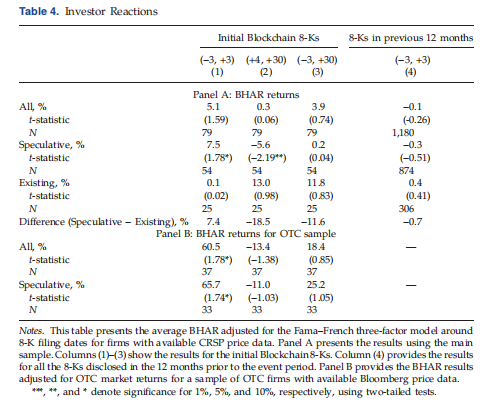
Riding the Blockchain Mania: Public Firms’ Speculative 8-aK Disclosures (MS2019)


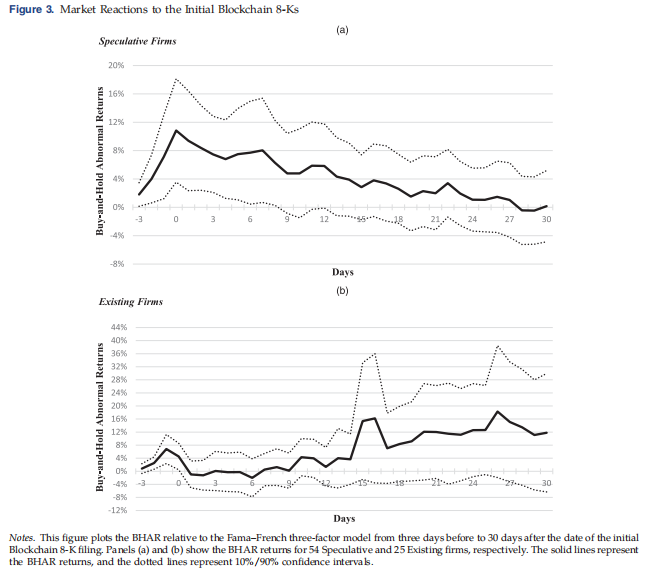
Sex, drugs, and bitcoin: How much illegal activity is financed through cryptocurrencies? (RFS2019)

-
Method
- Identifying a Sample of Illegal Users
- First approach: Bitcoin seizures by law enforcement agencies
- Second approach: Illegal darknet marketplaces and their users
- Third approach: Users identified in darknet forums
- Quantifying and Characterizing All Illegal Activity
- Method 1: Network cluster analysis (smart local moving algorithm, SLM)
- Method 2: Detection-controlled estimation (DCE)
- Identifying a Sample of Illegal Users
-
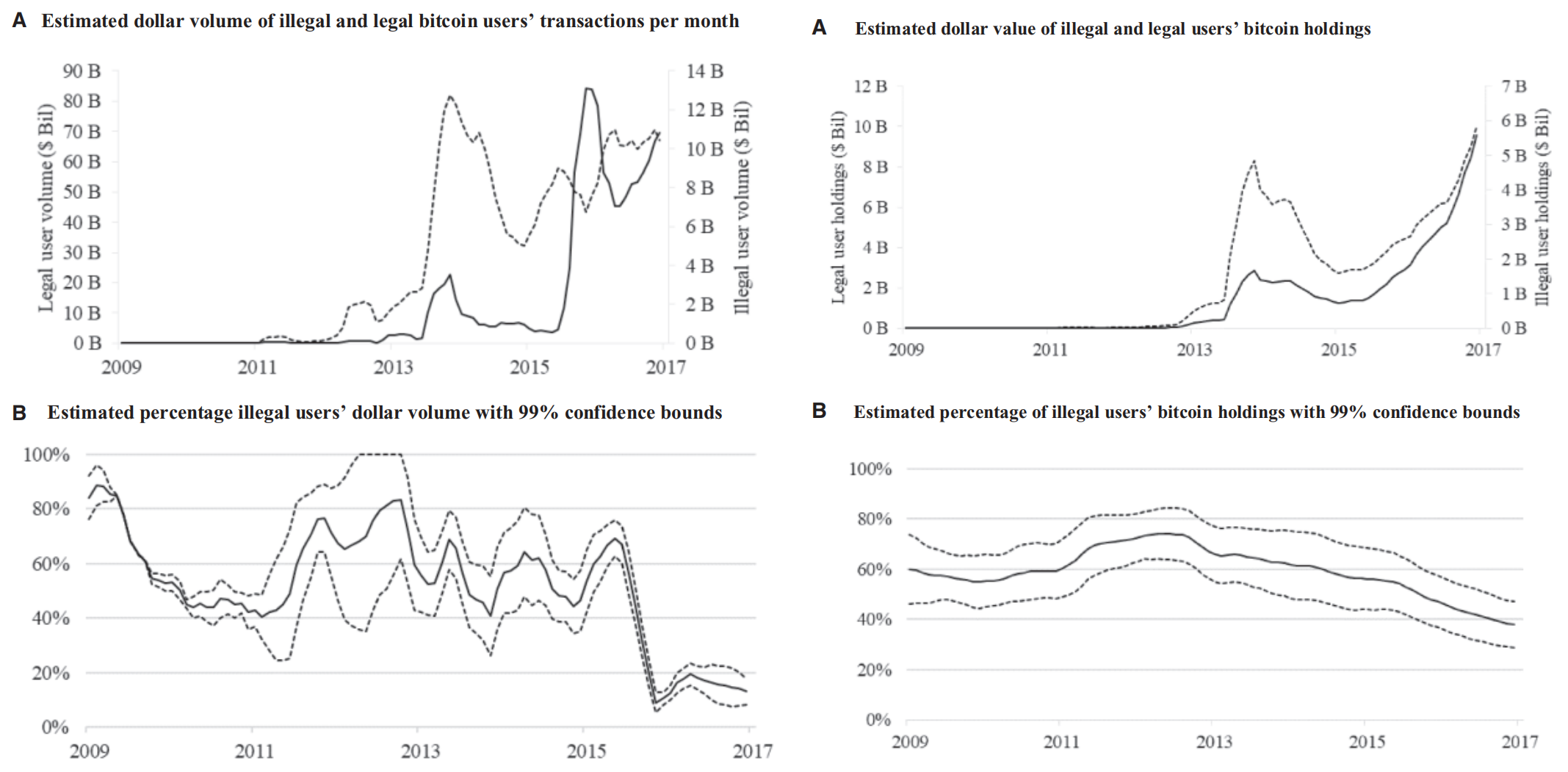
Results: How much illegal activity involves bitcoin?
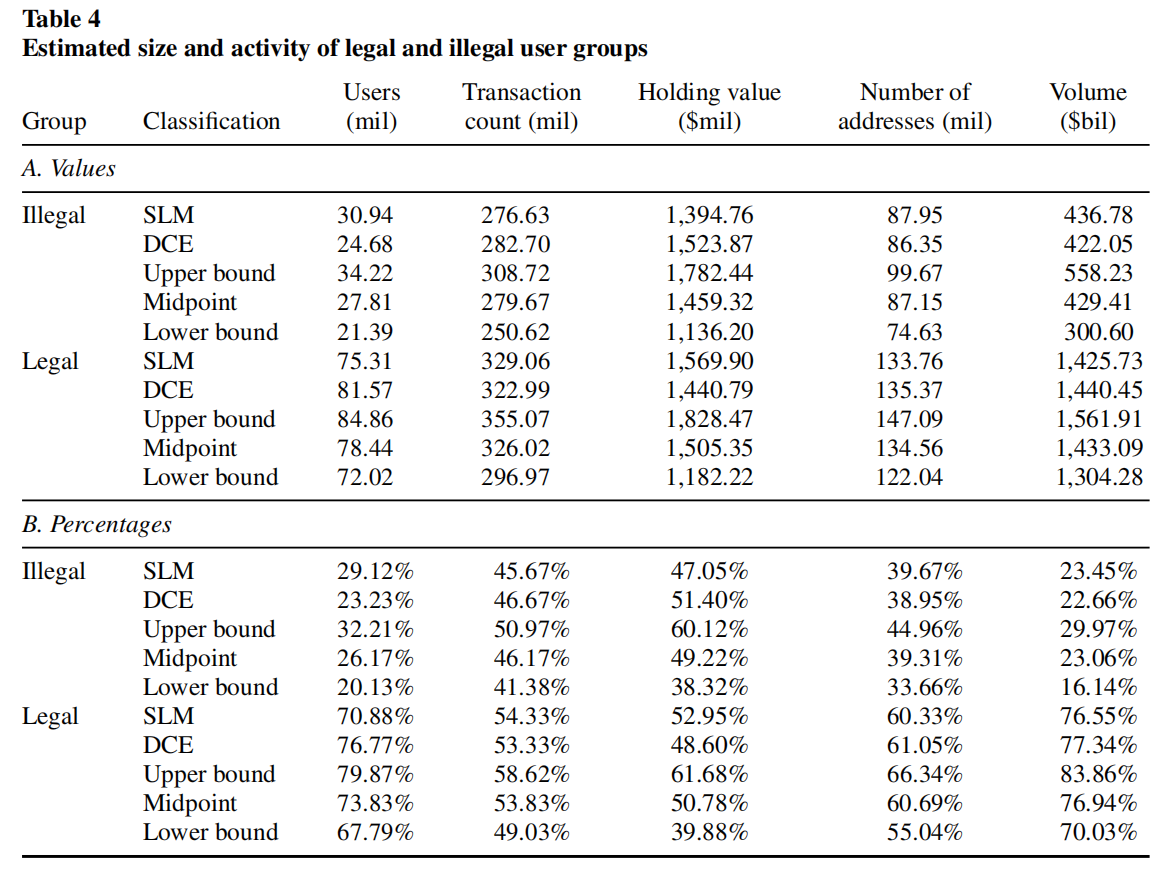
- Results: How does illegal activity vary through time?
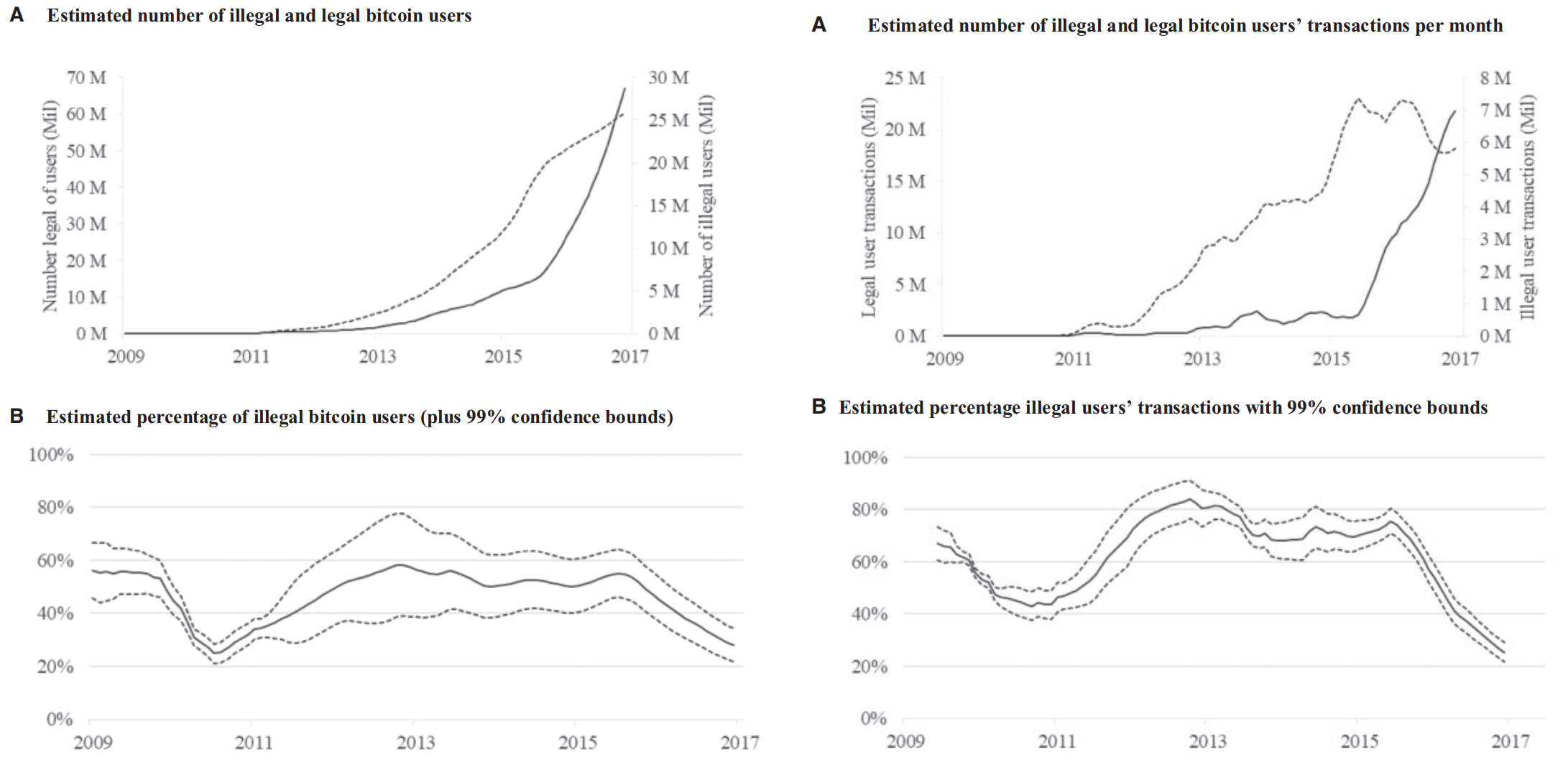
- Results: How does illegal activity vary through time?
Why BTC Will Fail to Scale (MS2022)

- the scaling problem
- Bitcoin throughput is limited by its block capacity
- approximately 2200 transactions were confirmed every 10 minutes
- BTC community is considering increase the block capacity
- The paper proves that it does not work
- Method
- a game theoretical model to analyze the strategic interactions of miners and users
- Results
- a relaxation of throughput congestion can facilitate large miners to tacitly collude
- artificially reducing the actualized throughput via the strategic partial filling of blocks to receive higher transaction fees
- technological intervention (such as banning large miners)
- can eliminate collusion
- makes the system less secure
- a relaxation of throughput congestion can facilitate large miners to tacitly collude
Decentralized Clearing via Blockchain (RFS2019)

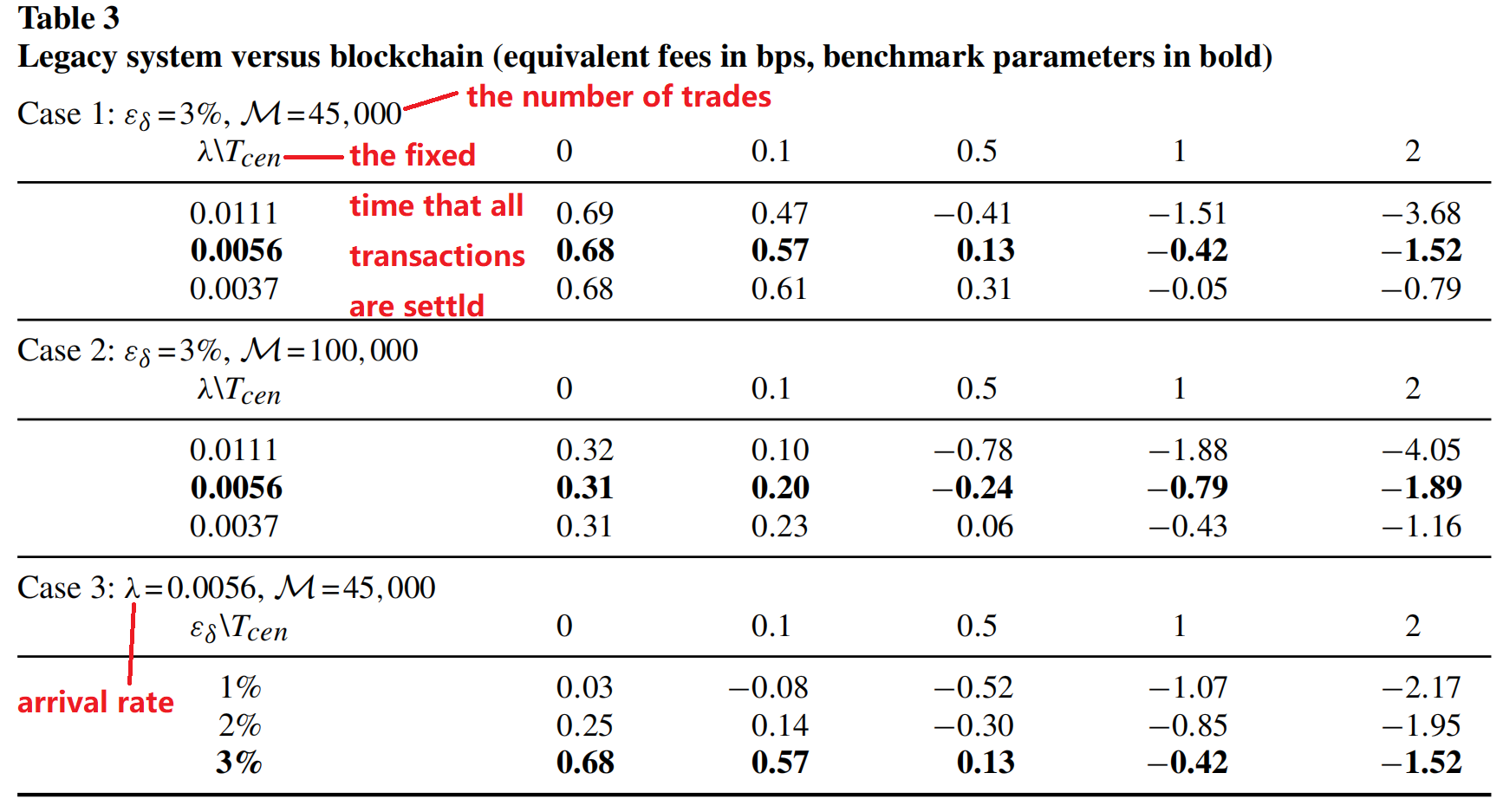
larger trading volume, higher time criticality, and lower default exposure make
settlement on a blockchain more attractive.
Common Risk Factors in Cryptocurrency (JF2022)

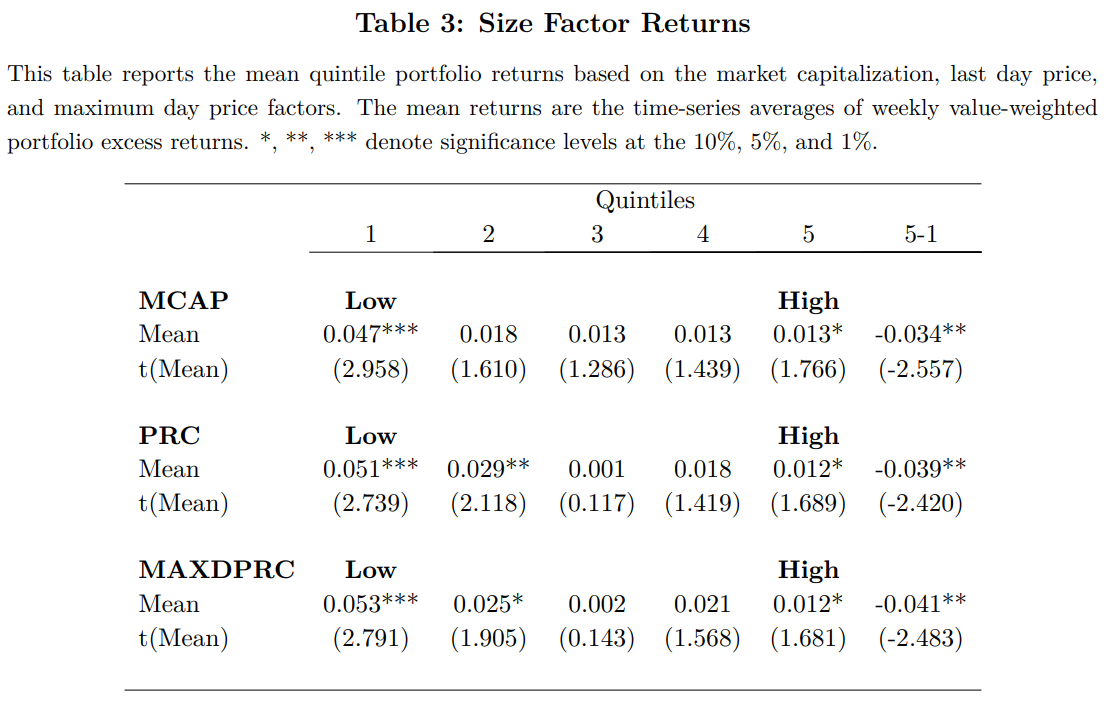
Cross-Sectional Factors
- Size Factor Returns
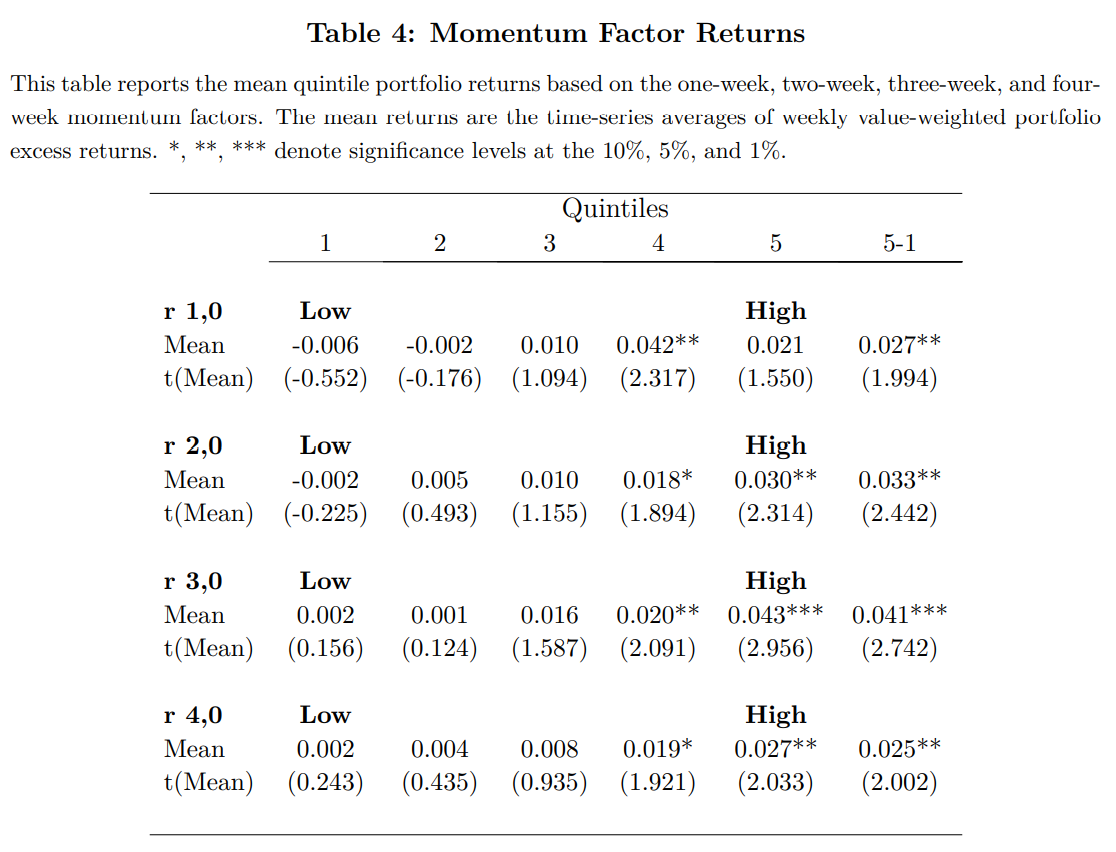
- Momentum Factor Returns
- Volume Factor Returns
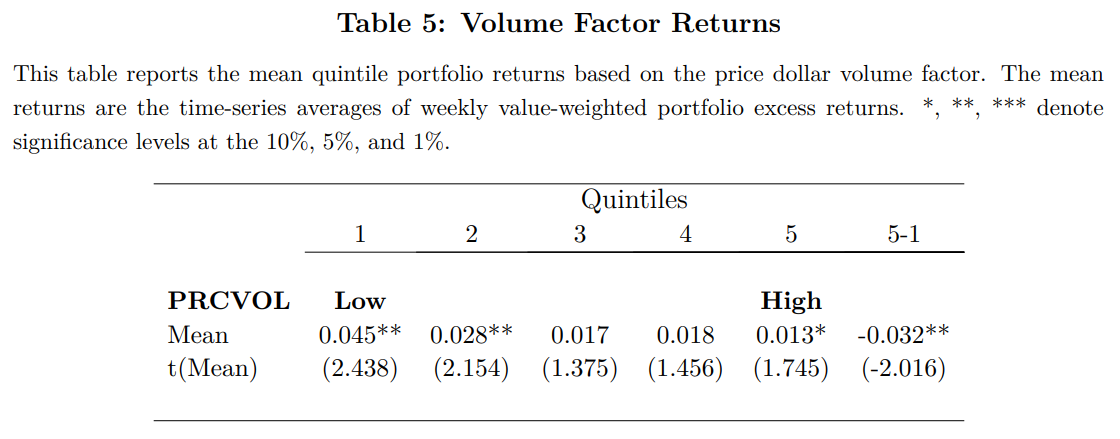
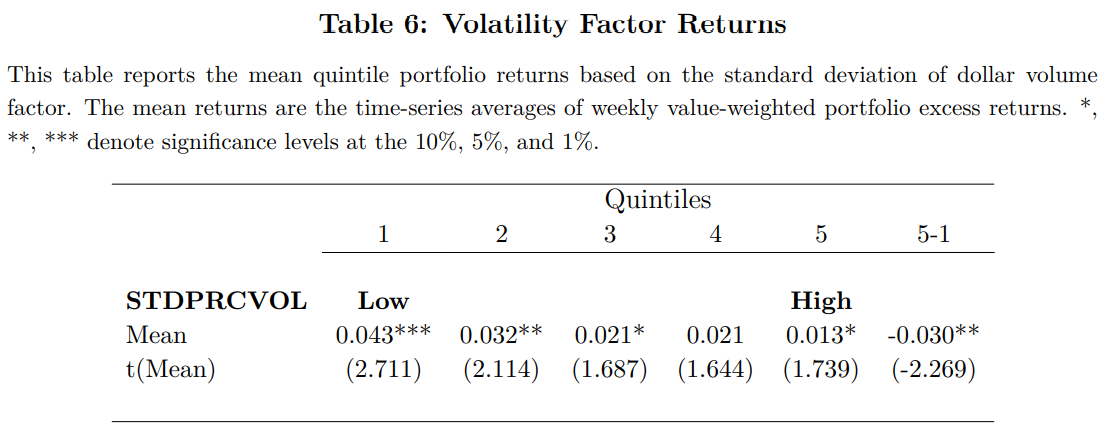
- Volatility Factor Returns
Cryptocurrency Factors
- Cryptocurrency One-Factor Model

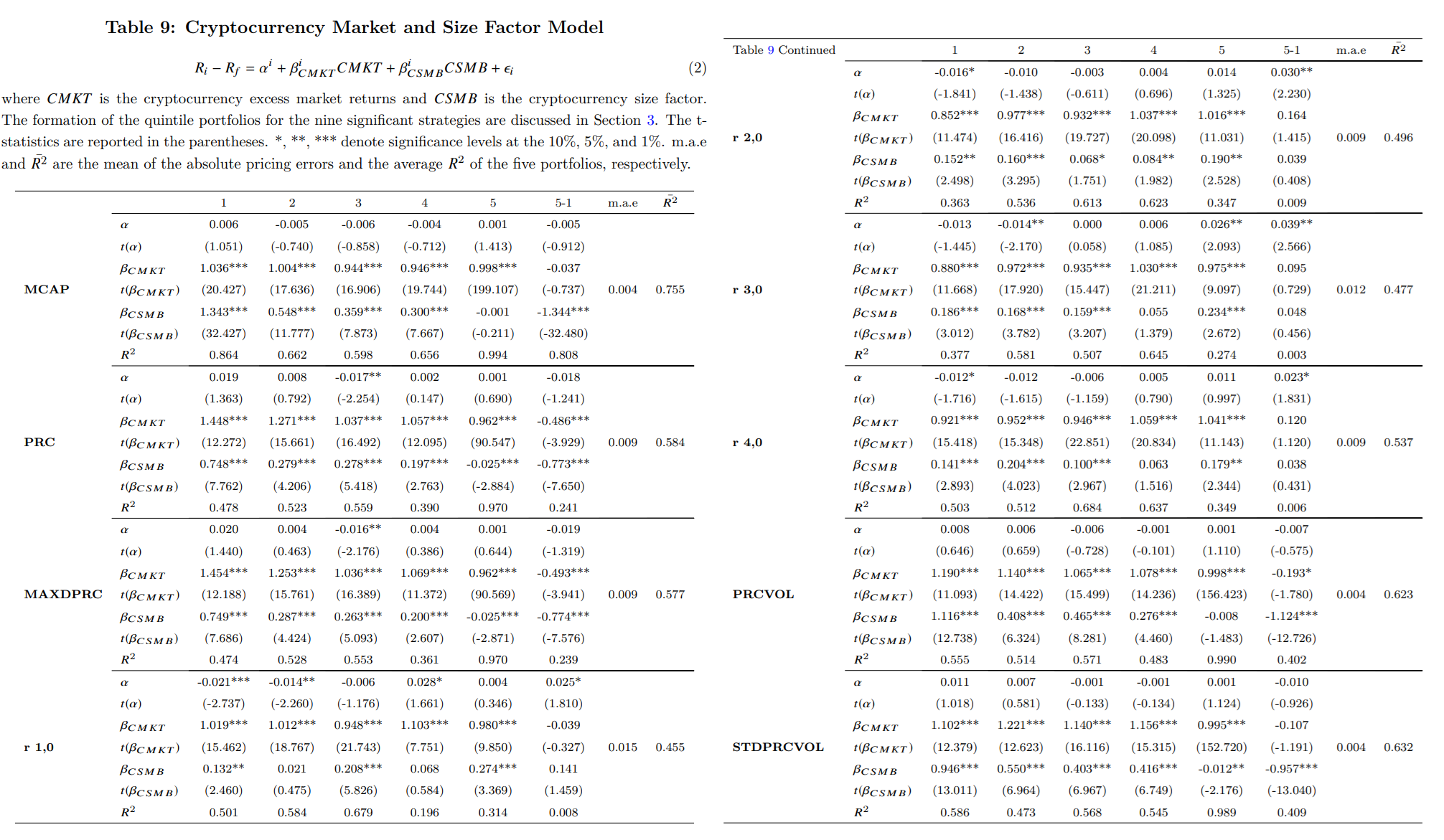
- Cryptocurrency Market and Size Factor Model
- Cryptocurrency Market and Momentum Factor Model

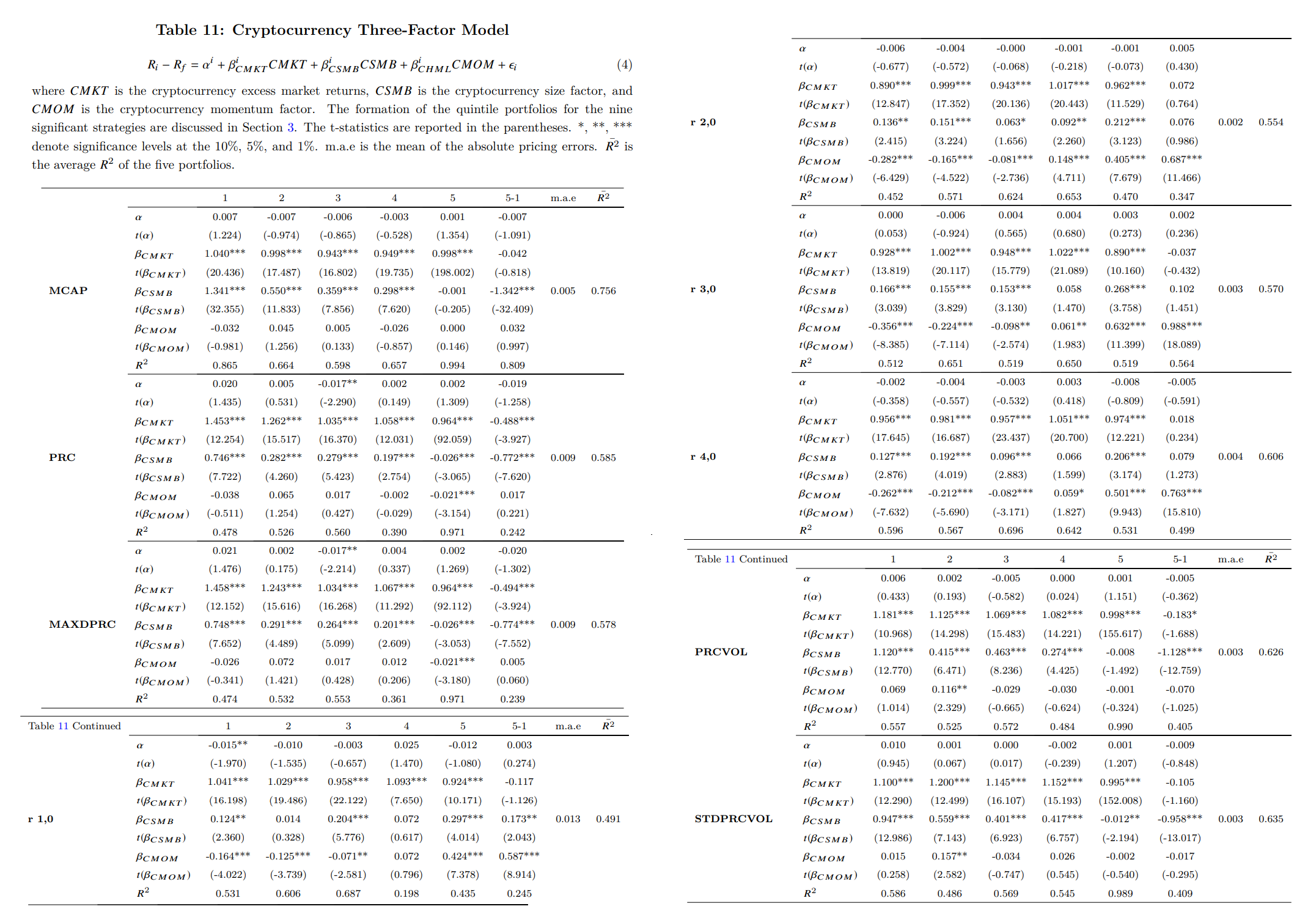
- Cryptocurrency Three-Factor Model
Is Bitcoin Really Untetherd? (JF2020)

-
Two main alternative hypotheses for Tether
- Tether is “pulled” (demand-driven): Tether is driven by legitimate demand from investors who use Tether as a medium of exchange to enter their fiat capital into the cryptospace because it is digital currency with the stability of the dollar “peg.” In this case, the price impact of Tether reflects natural market demand.
- Tether is “pushed” (supply-driven) : Bitfinex prints Tether regardless of the demand from cash investors, and additional supply of Tether can create inflation in the price of Bitcoin that is not due to a genuine capital flow.
-
Motivations for "push"
- The Tether creators, like most early cryptocurrency adopters and exchanges, have large holdings of Bitcoin, they generally profit from the inflation of the cryptocurrency prices.
- Coordinated supply of Tether creates an opportunity to manipulate cryptocurrencies—when prices are falling, the Tether creators can convert their large Tether supply into Bitcoin in a way that pushes Bitcoin up and then sell some Bitcoin back into dollars in a venue with less price impact to replenish Tether reserves.
- If cryptocurrency prices crash, the founders essentially have a put option to default on redeeming Tether, or to potentially experience a “hack” or insufficient reserves where by Tether-related dollars disappear.
Figure 1 Aggregate flow of Tether between major addresses.

-
Main Hypotheses:
- H1A:Tether's price relative to the USD may increase as a consequence of strong investor demand. Tether flows should be strongly related to this demand as proxied by changes in the Tether-USD exchange rate.
- H1B:The printing of Tether may also be driven by its usefulness as a facilitator of cross-exchange arbitrage to eliminate pricing discrepancies across cryptocurrency exchanges. For example, Tether outflows from Bitfinex to another exchange should correspond to periods when Bitcoin sells at a premium on Bitfinex relative to that exchange.
-
To examine the “push” hypothesis, the authors test the following predictions:
- H2A:If Tether issuers are trying to provide stability to the market during downturns, outflows of Tether and purchases of Bitcoin by Bitfinex may follow periods of negative Bitcoin returns.
- H2B:If Tether supply is large enough to have a material price impact on Bitcoin, Bitcoin prices should go up after Tether flows into the market, especially after periods with large authorization of Tether.
- H2C:Bitcoin returns may show a return reversal after negative returns, especially during times when Tether flows into the market.
- H2D:Since round-number thresholds can be price anchors to set a price floor and are often used as buying signals by investors, flow of Tether might increase if Bitcoin falls below these salient round-number thresholds. This effect should be more pronounced in periods with large Tether authorization.
- H2E:If Tether is not fully backed by dollars at the outset, but the issuers want to signal otherwise to investors by releasing EOM (or other interval) accounting statements, then Tether creators may liquidate Bitcoins into USD to demonstrate sufficient reserves. This could create negative returns in Bitcoin at the EOM, particularly in periods with large Tether issuances.
Figure 5 Prices of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies around high-flow events.
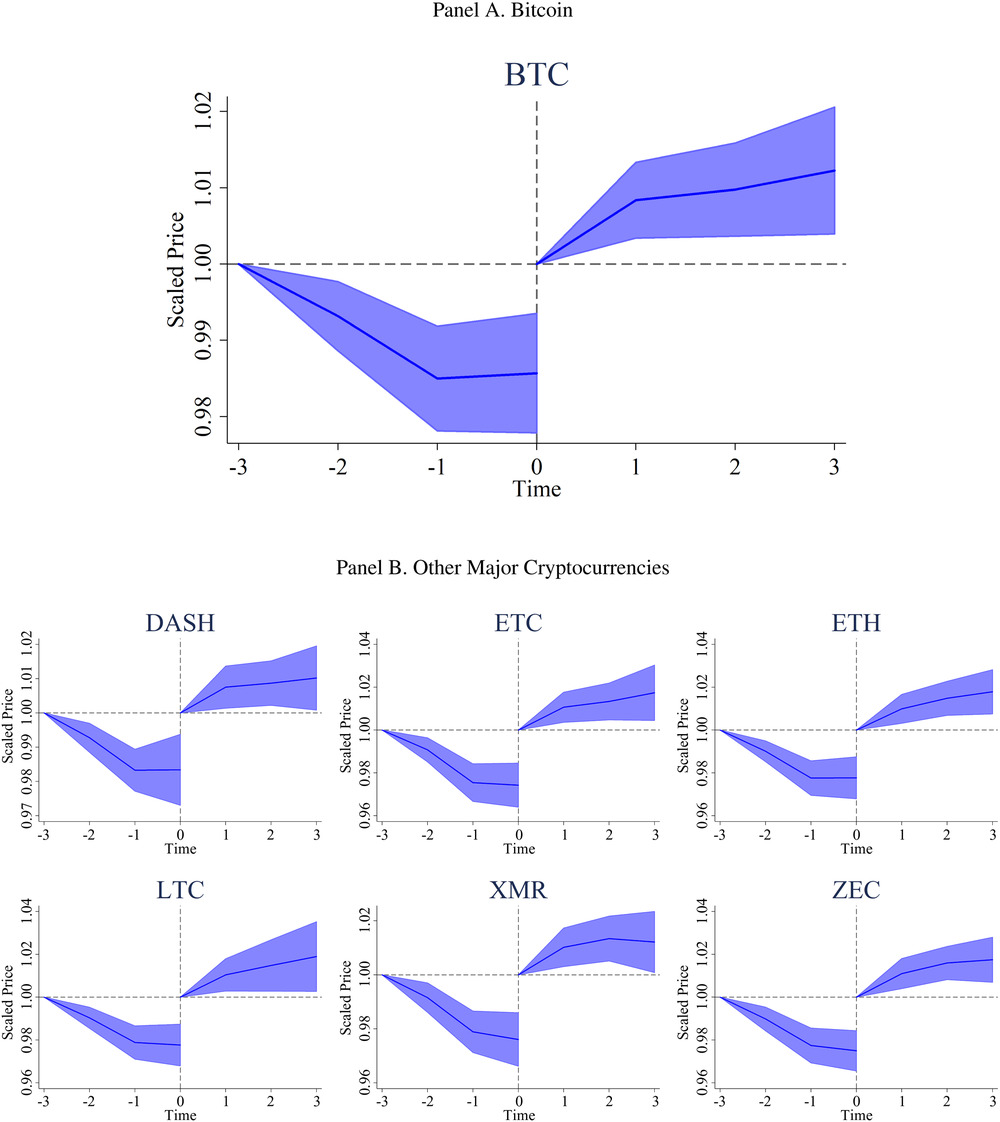
Panel A shows Bitcoin prices three hours before and after the top 1% of high-flow hours to Poloniex and Bittrex. Prices are scaled to one at time −3 before the event and at time 0 at the end of the event window. Scaled prices are averaged across events. High-flow events are defined as the top 1% of hours with high net average flows of Tether from Bitfinex to Poloniex and Bittrex and Bitcoin back from Poloniex and Bittrex to Bitfinex in the prior hour, which means that high flows occur between time −1 and time 0. Panel B depicts similar results for other major cryptocurrencies.