The Timeline of Ethereum¶

资讯
软件
Ethereum is the foundation for a new era of the internet:
An internet where money and payments are built in.
An internet where users can own their data, and your apps don’t spy and steal from you.
An internet where everyone has access to an open financial system.
An internet built on neutral, open-access infrastructure, controlled by no company or person.
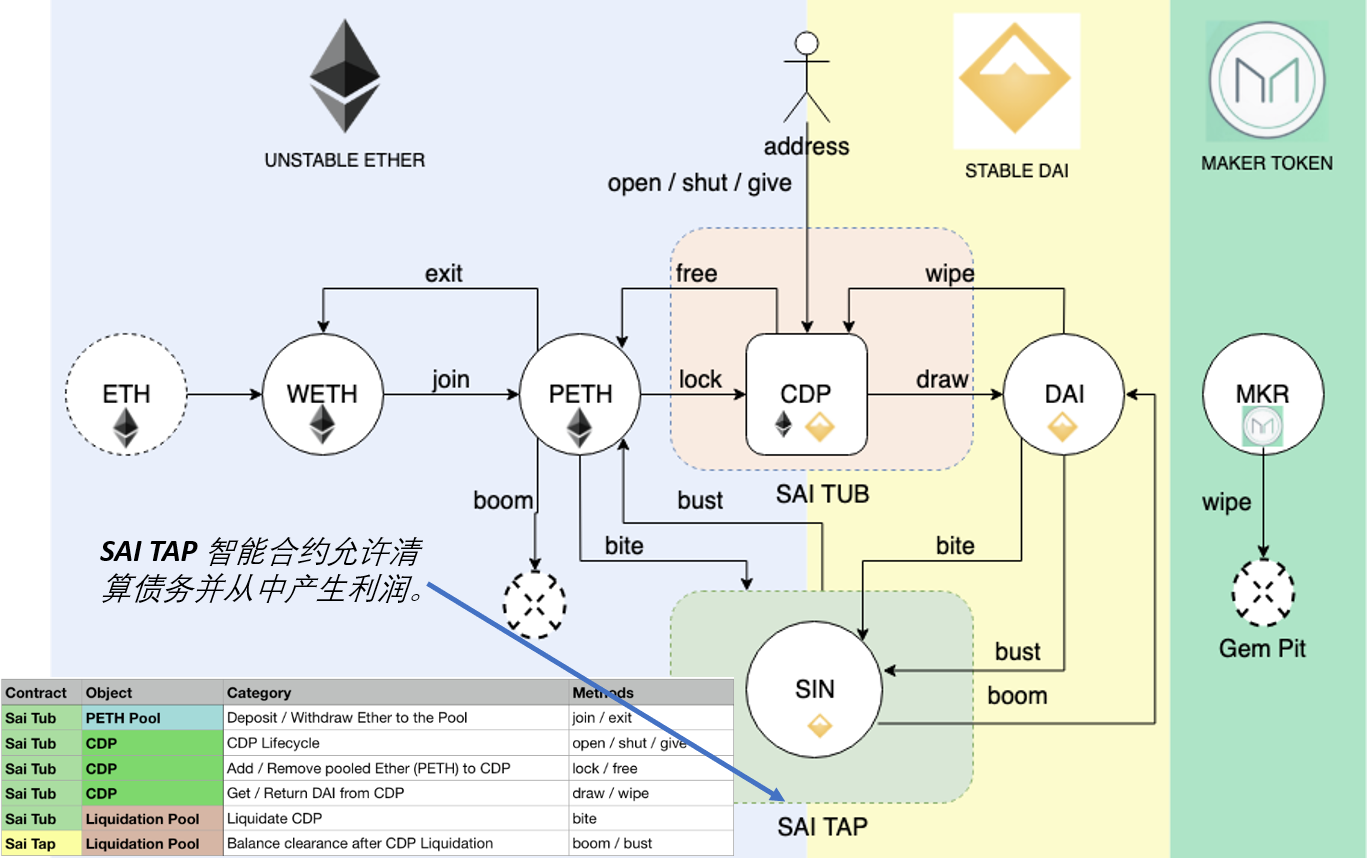
Ethereum’s development was planned over four distinct stages, with major changes occurring at each stage. A stage may include subreleases, known as "hard forks," that change functionality in a way that is not backward compatible.
The four main development stages are codenamed Frontier, Homestead, Metropolis, and Serenity. The intermediate hard forks that have occurred (or are planned) to date are codenamed Ice Age, DAO, Tangerine Whistle, Spurious Dragon, Byzantium, and Constantinople. Both the development stages and the intermediate hard forks are shown on the following timeline, which is "dated" by block number:
Block #0: Frontier—The initial stage of Ethereum, lasting from July 30, 2015, to March 2016.
Block #200,000: Ice Age—A hard fork to introduce an exponential difficulty increase, to motivate a transition to PoS when ready.
Block #1,150,000: Homestead—The second stage of Ethereum, launched in March 2016.
Block #1,192,000: DAO—A hard fork that reimbursed victims of the hacked DAO contract and caused Ethereum and Ethereum Classic to split into two competing systems.
Block #2,463,000: Tangerine Whistle—A hard fork to change the gas calculation for certain I/O-heavy operations and to clear the accumulated state from a denial-of-service (DoS) attack that exploited the low gas cost of those operations.
Block #2,675,000: Spurious Dragon—A hard fork to address more DoS attack vectors, and another state clearing. Also, a replay attack protection mechanism.
Block #4,370,000: Metropolis Byzantium—Metropolis is the third stage of Ethereum, current at the time of writing this book, launched in October 2017. Byzantium is the first of two hard forks planned for Metropolis.
After Byzantium, there is one more hard fork planned for Metropolis: Constantinople. Metropolis will be followed by the final stage of Ethereum’s deployment, codenamed Serenity.

In Ethereum, the components of a blockchain system described in Components of a Blockchain are, more specifically:
P2P network
Consensus rules
Transactions
State machine
Data structures
Consensus algorithm
Economic security
Clients
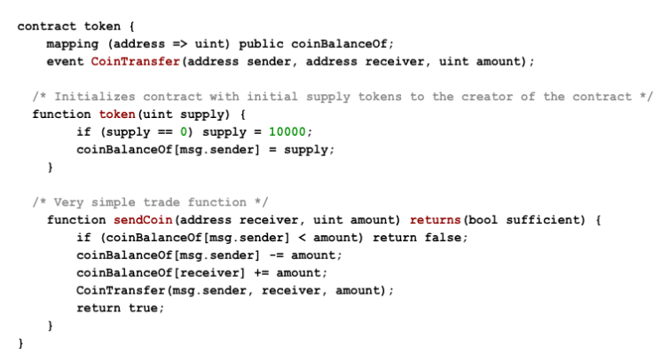
Ethereum is a decentralized platform for creating smart contracts, which are stored in a blockchain. The Ethereum Virtual Machine is an isolated runtime environment that hosts these contracts. Ethereum’s network infrastructure uses the cryptocurrency Ether to facilitate transactions.
Smart contracts are programs that are coded to automatically control the transfer of assets between two or more parties, once predefined conditions have been met. They are designed to safely and transparently facilitate the exchange of assets, without the need for a middleman.
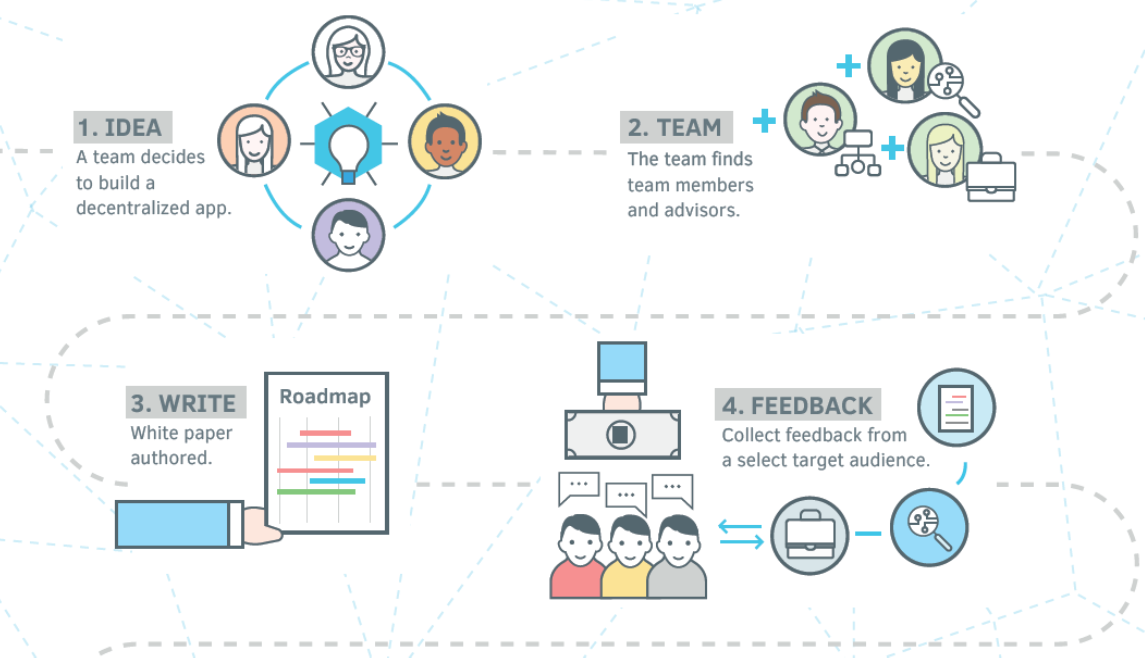
A DApp is composed of at least:
Smart contracts on a blockchain
A web frontend user interface
In addition, many DApps include other decentralized components, such as:
A decentralized (P2P) storage protocol and platform
A decentralized (P2P) messaging protocol and platform
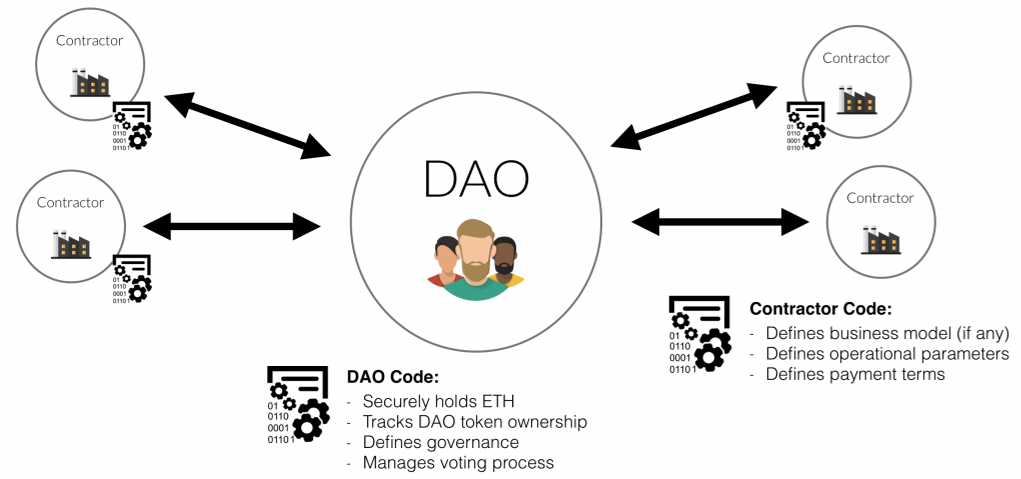
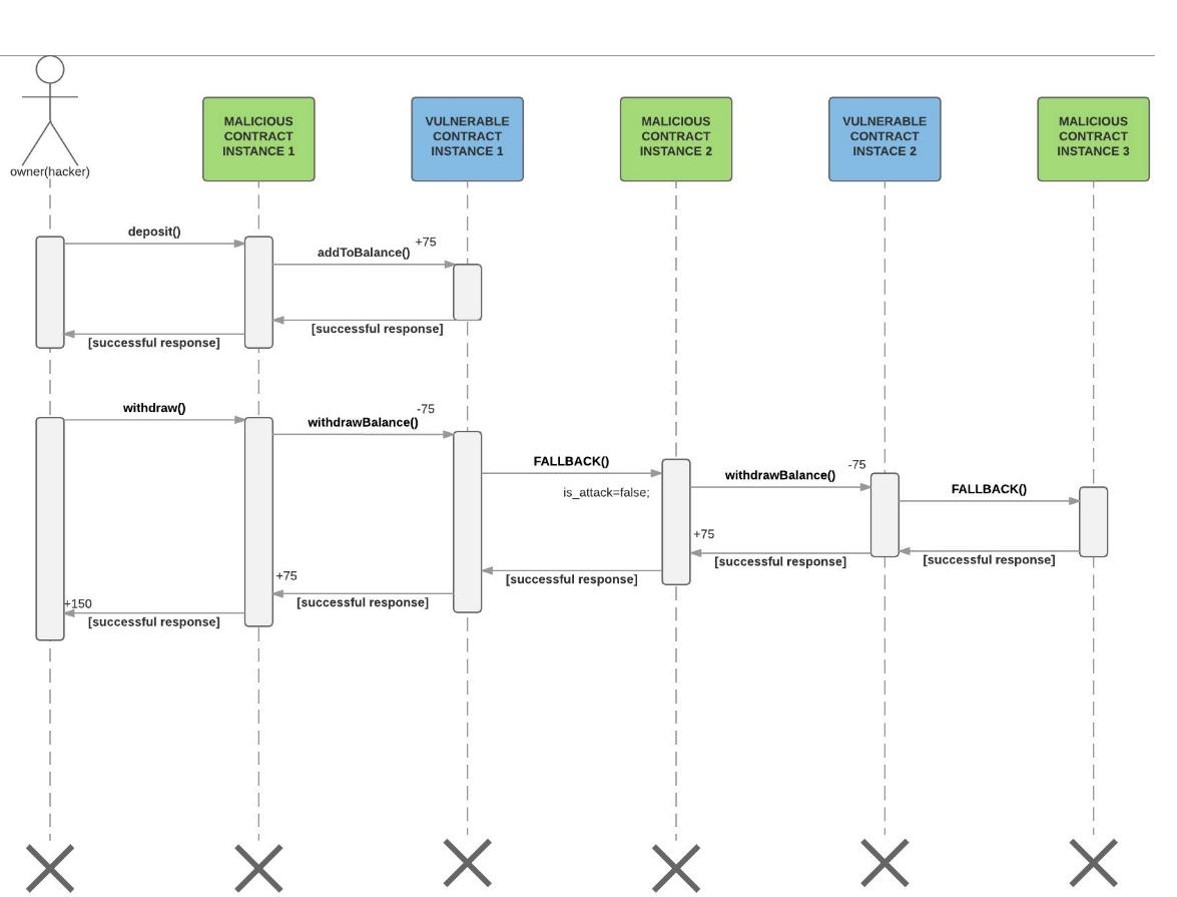
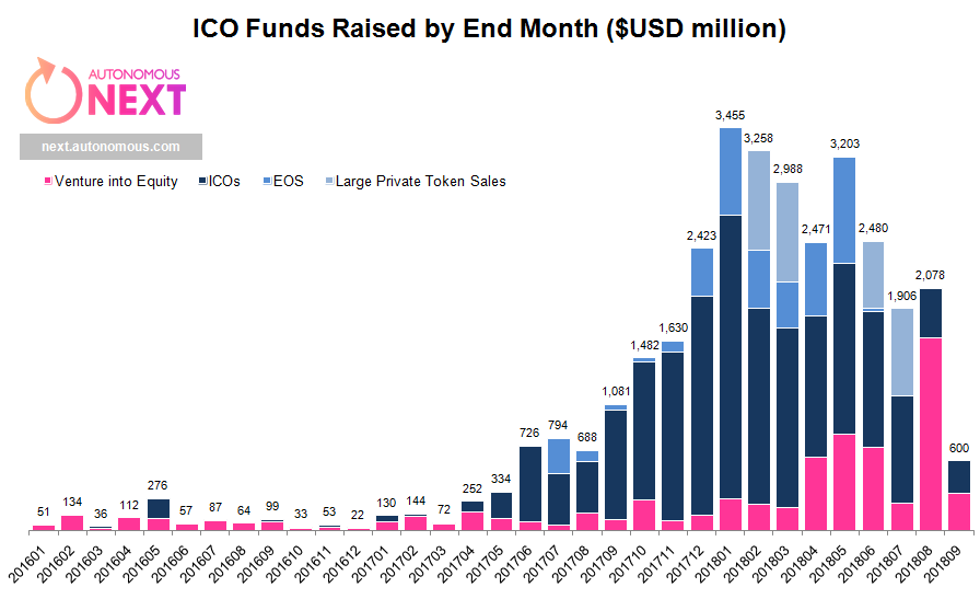
The DAO raised USD 150mn in ETH during May 2016. On 17 June 2016, the DAO was hacked and USD 50mn stolen by exploiting recursive call vulnerabilities.


| 排名 | 数字货币 | 总市值 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bitcoin | 126,387,557,616 |
| 2 | Ethereum | 17,502,341,386 |
| 3 | XRP | 8,302,309,107 |
| 4 | Tether | 6,370,220,958 |
| 5 | Bitcoin Cash | 4,144,031,574 |
| 6 | Bitcoin SV | 3,515,738,866 |
| 7 | Litecoin | 2,673,016,498 |
| 8 | Binance Coin | 2,443,269,109 |
| 9 | EOS | 2,270,807,037 |
| 10 | Tezos | 1,375,470,401 |
| 排名 | 数字货币交易所 | 成交量 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bitfinex | 49,230,727 |
| 2 | HitBTC | 46,356,768 |
| 3 | Binance | 42,345,655 |
| 4 | Huobi Global | 38,795,263 |
| 5 | Kraken | 24,655,403 |
| 6 | ZB.COM | 20,941,182 |
| 7 | Folgory | 17,235,333 |
| 8 | BW.com | 15,777,310 |
| 9 | OKEx | 13,677,201 |
| 10 | Huobi Russia | 12,526,382 |
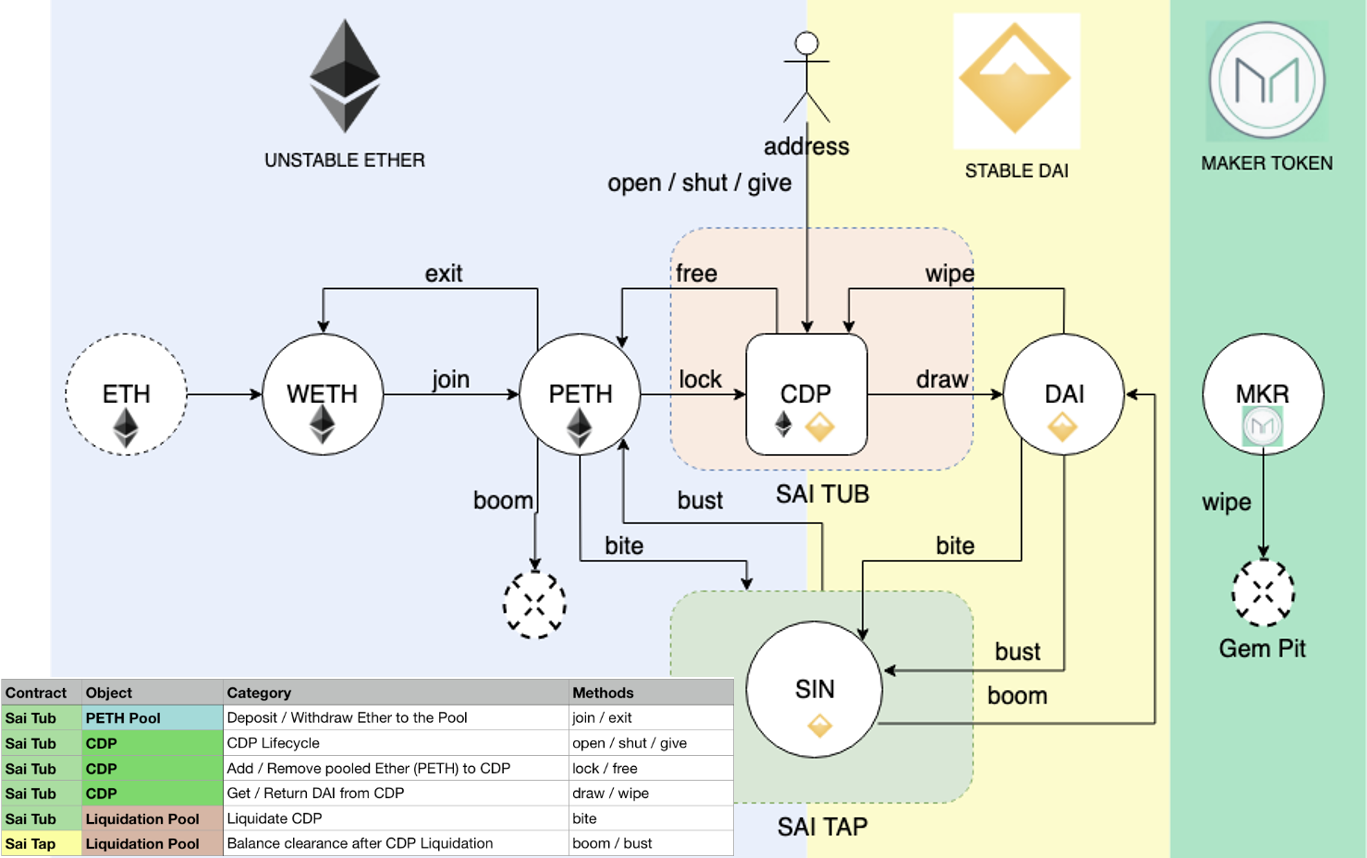
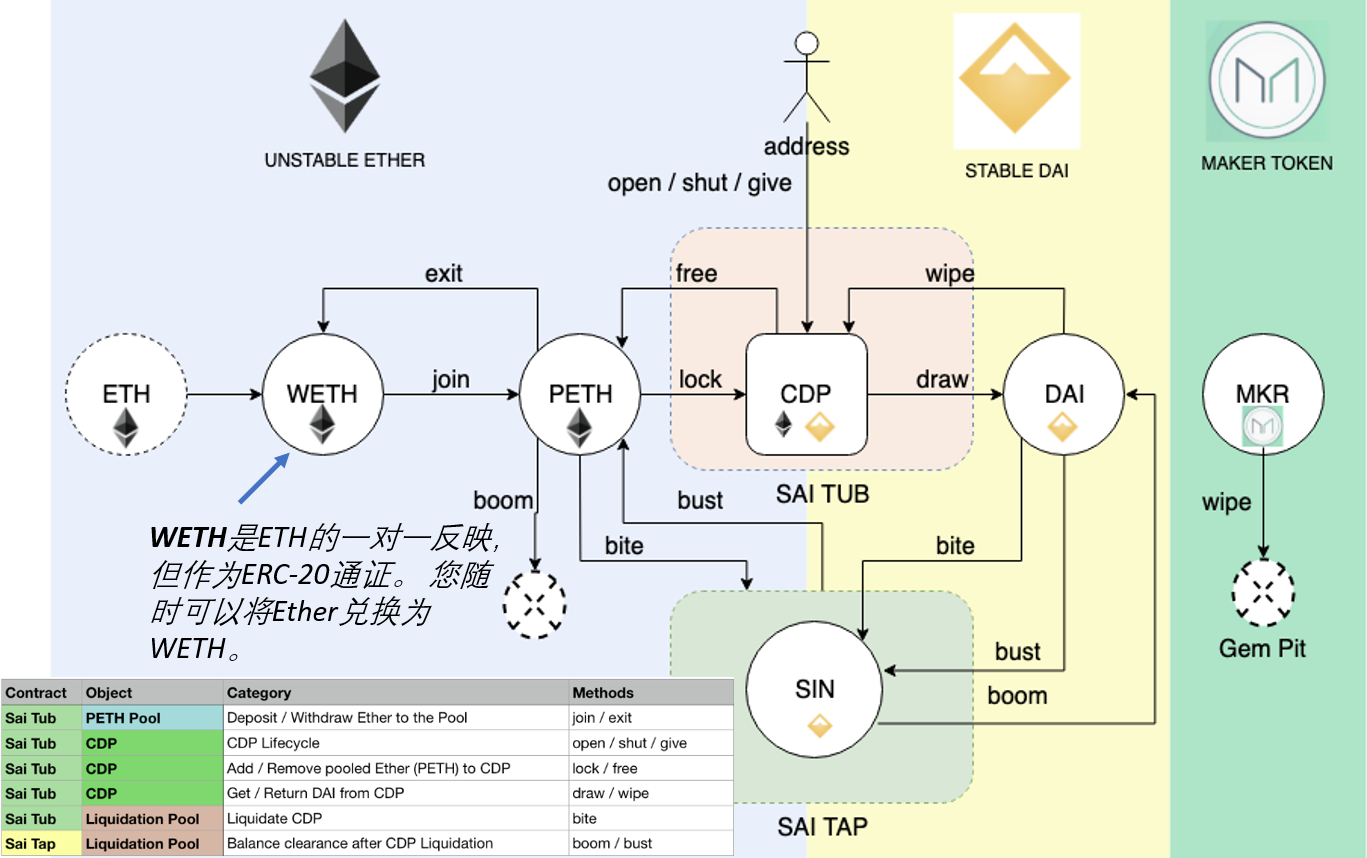
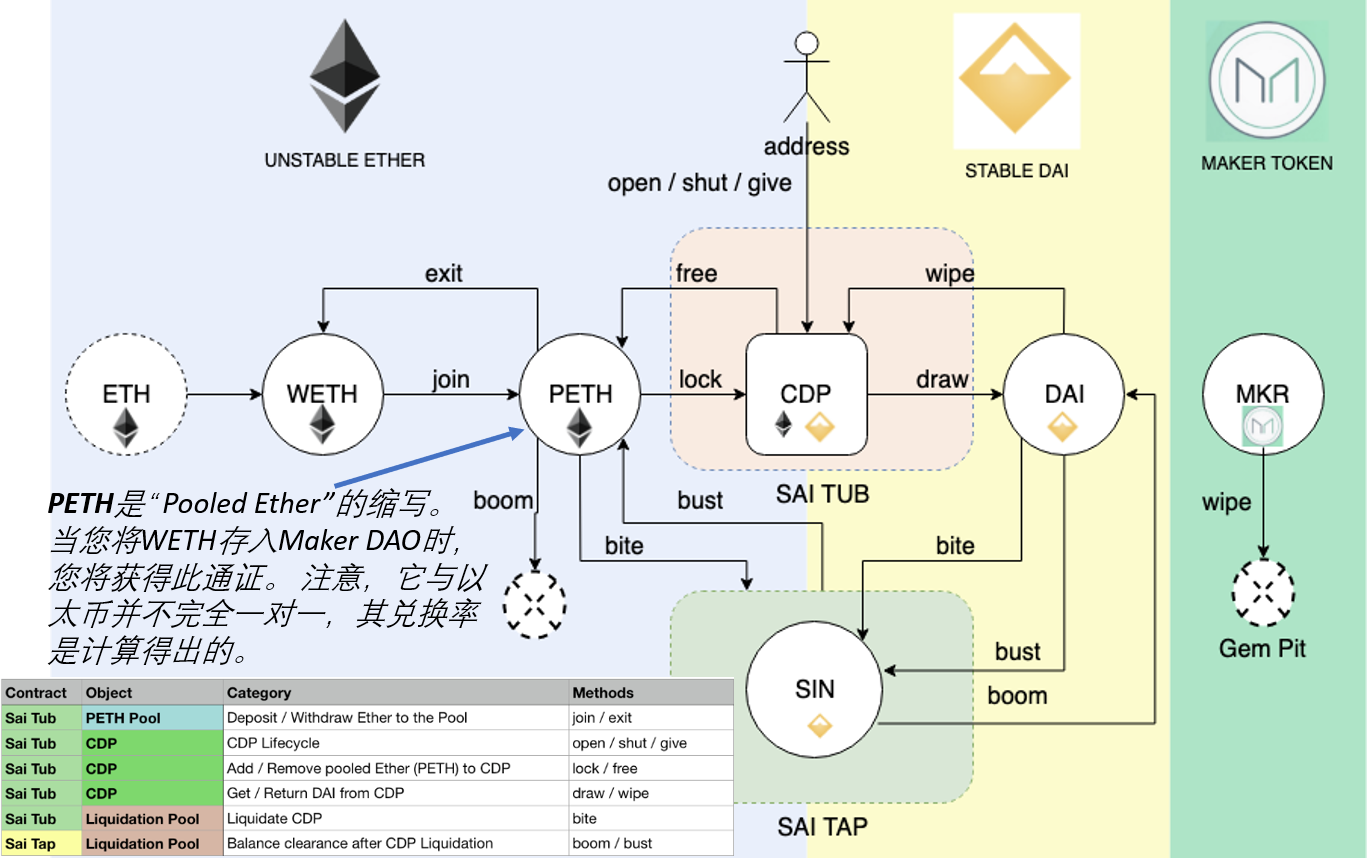
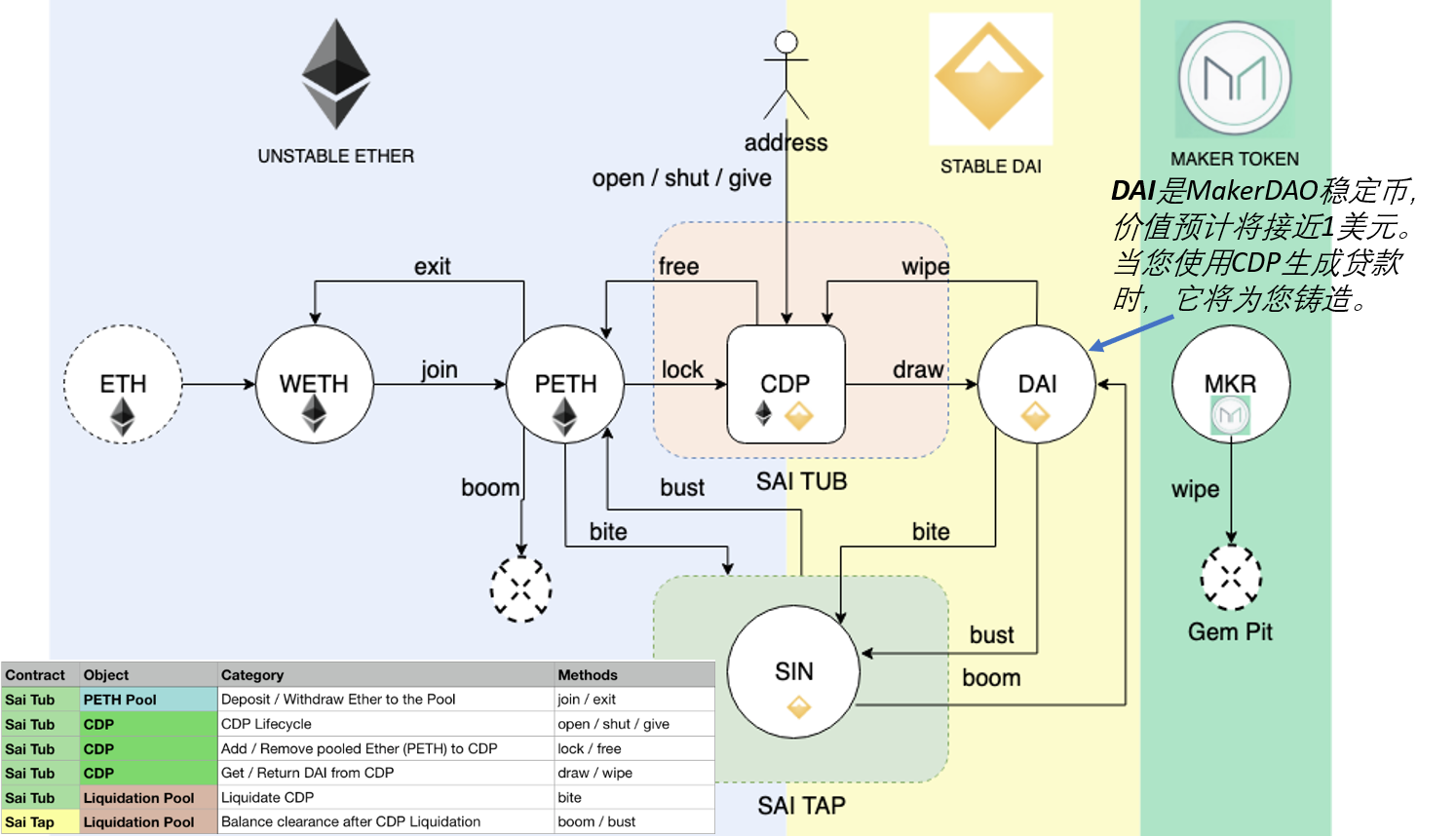
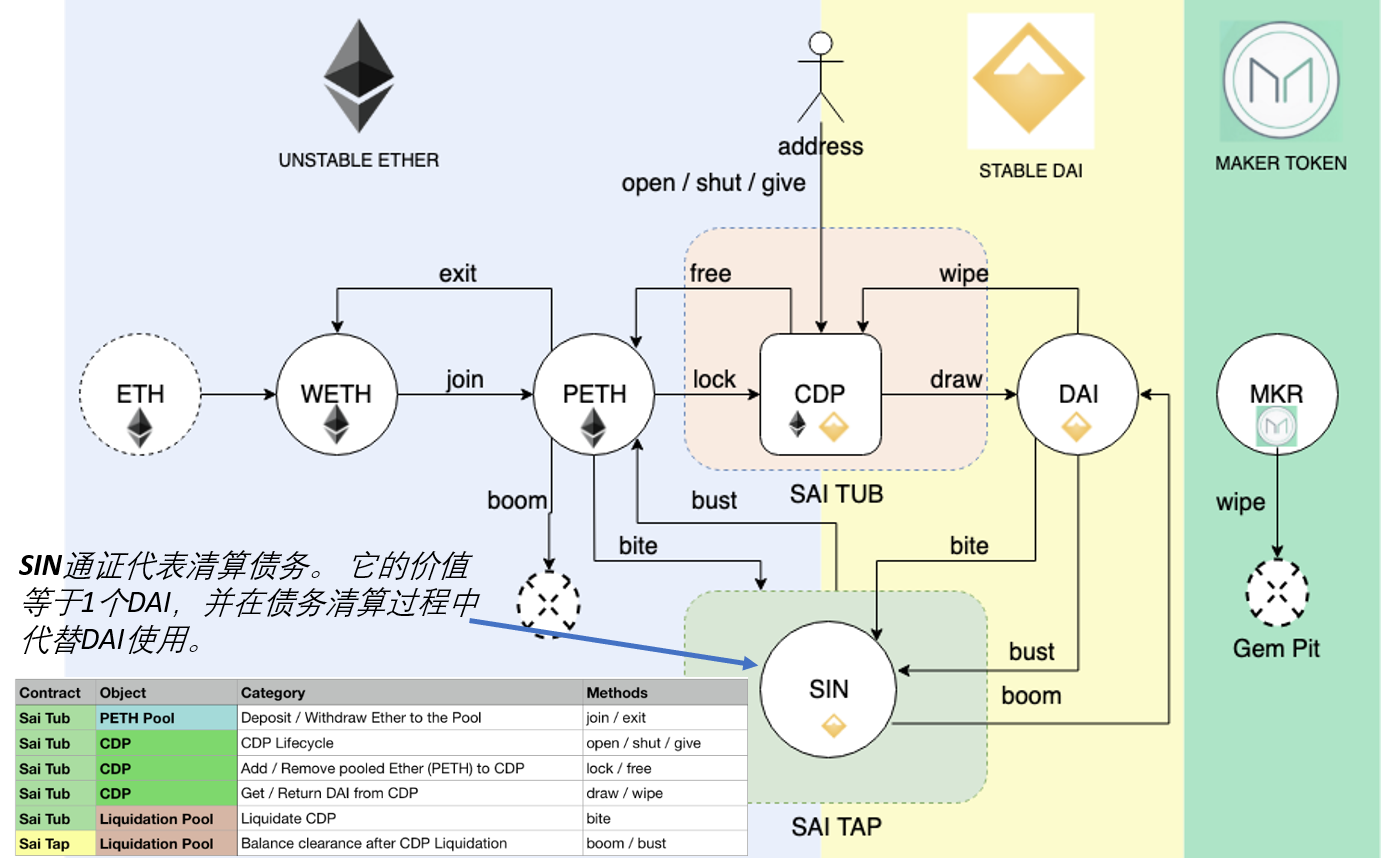
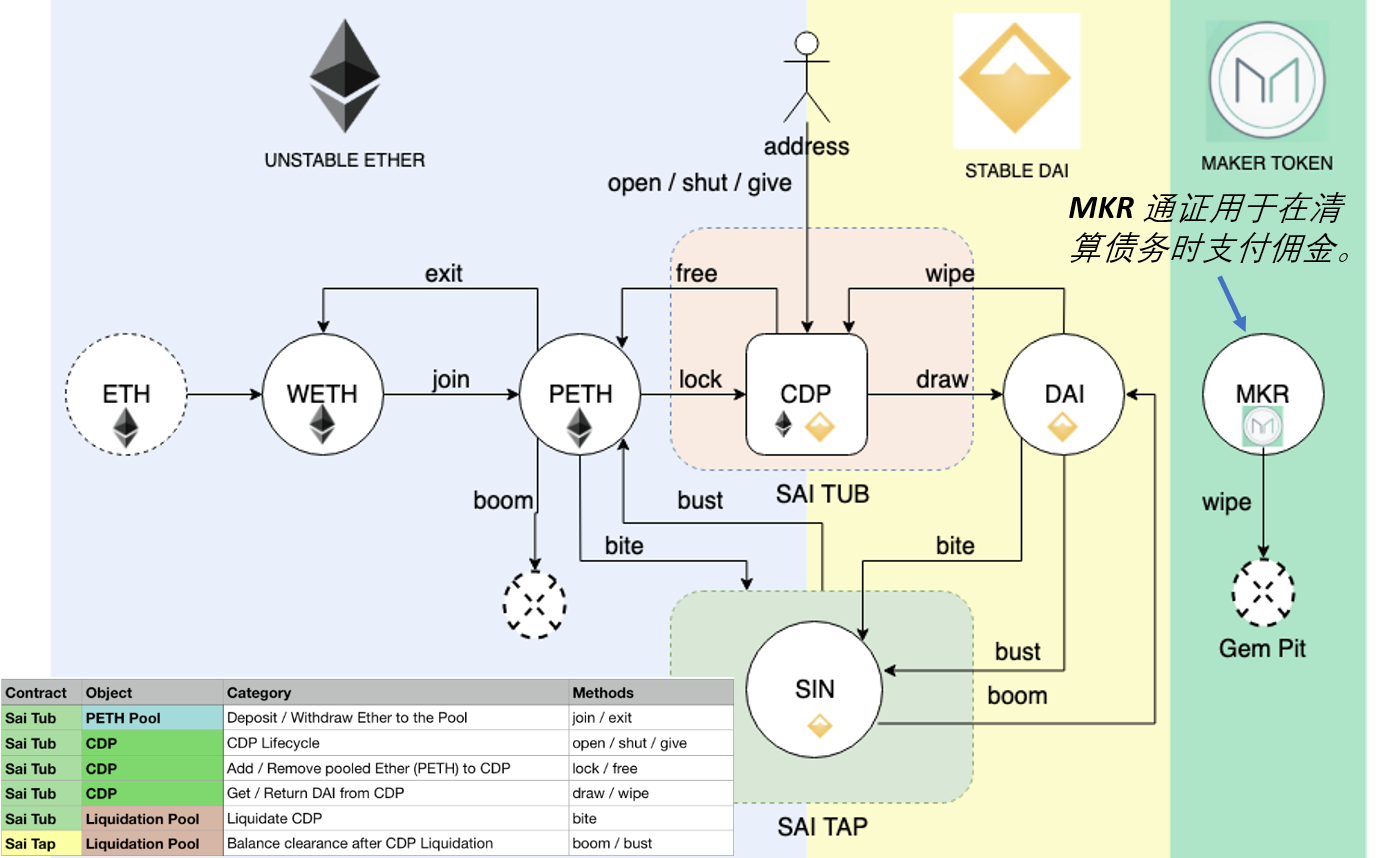
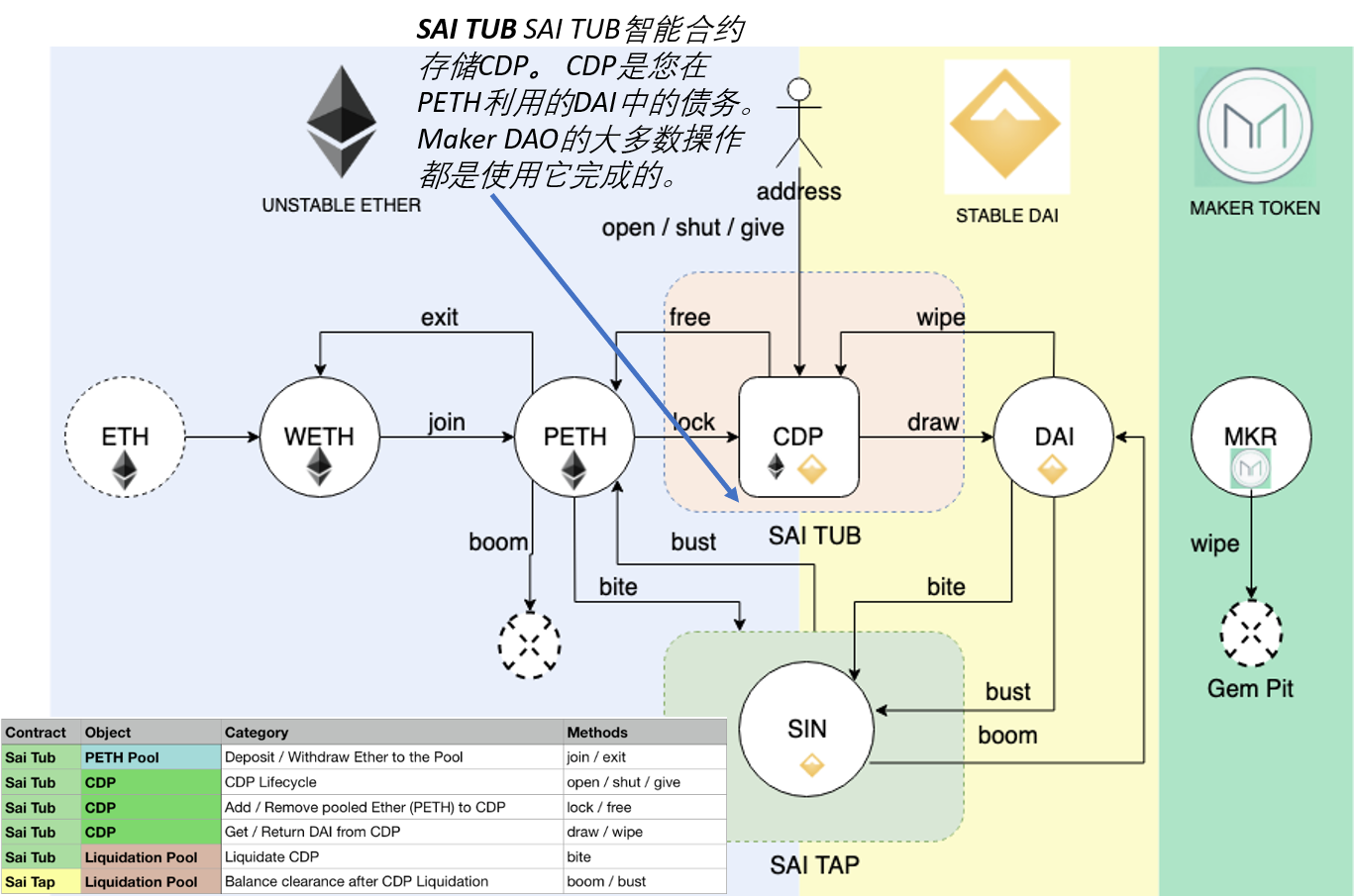
CDP持有用户存放的抵押资产,并允许该用户生成Dai,但生成Dai也会产生债务。 这笔债务有效地将存入抵押品的资产锁定在CDP内,直到后来通过偿还等额的Dai来弥补它为止,此时所有者可以再次提取其抵押品。 活跃CDP总是抵押过多,这意味着抵押物的价值高于债务的价值。 (Maker DAO的要求:150%)